How psychological factors influence health-promoting behaviors?
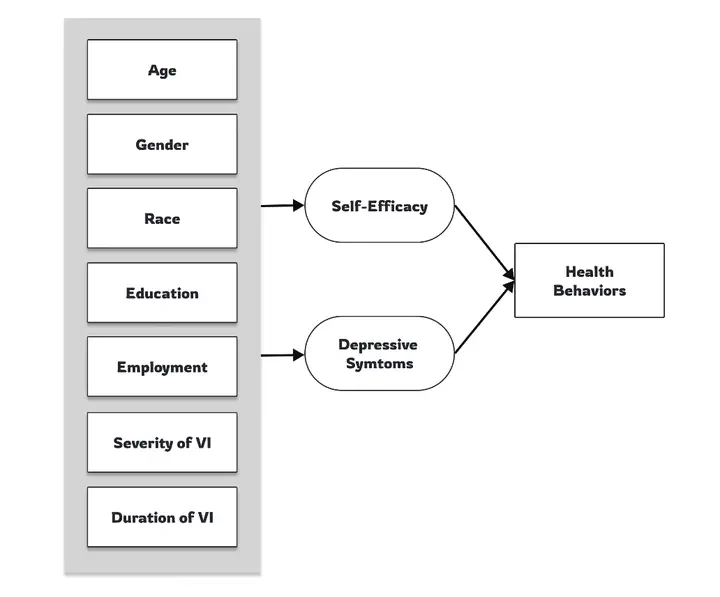 Conceptual Model of the Study
Conceptual Model of the StudyThe current study utilized the Transtheoretical Model of Behavioral Change to investigate the influence of self-efficacy and depressive symptoms on health-promoting behaviors in adults with visual impairments (VI). We hypothesized that these psychological factors, in conjunction with covariates such as age, gender, race, education level, employment status, severity of VI, and duration of VI, would be significantly associated with health-promoting behaviors, with gender serving as a potential moderator. We conducted a cross-sectional exploratory study via an online survey from September 1 to October 2, 2023, involving 2,667 participants (Mage = 36.33, SD = 9.30; analyzed N = 2,491). Of these, 2,282 participants (91.6%) had moderate to severe low vision, and 209 participants (8.4%) were blind. The analysis revealed that increased self-efficacy was linked to fewer depressive symptoms and reduced engagement in health behaviors. Higher levels of depressive symptoms correlated with poorer health behaviors. Significant gender differences were identified, implying a necessity for health behavior interventions tailored to the psychological and gender-specific needs of the visually impaired population to enhance their overall health and well-being.
- Keywords: blindness, health disparities, health promotion, low vision, mental health, self-efficacy